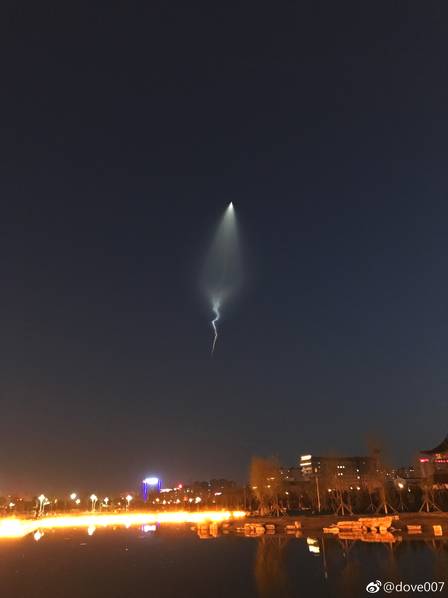
Americans are REACTIVATING their World War 1 era radio navigational system after their GPS Satellites fell behind Chinese BDS! LOL!
http://mil.news.sina.com.cn/jssd/2018-06-25/doc-ihencxtt9281159.shtml
美GPS导航系统难掩退步 受我北斗系统影响重启无线电
2018年06月25日 18:19
新浪军事
0
作为目前世界上综合军事能力的美国,在军事领域拥有远远高于其他国家的能力。一般的感觉就是,当我们开始装备某种武器,或者开始研究某个领域的时候,美国人已经率先在这一方面进行了许多年的研究了,要不美国人是怎么做到领先所有国家呢。经过六十多年的发展,全球定位系统,也就是人们常说的GPS已经成为了目前人类最为完善的全球导航系统。GPS最早在上个世纪五十年代末起源于美国国防部的项目,在六十年代中期投入使用,并开始向全球民用市场提供实时、全天候和全球性的导航服务。现在对于我们普通人来说,几乎已经离不开导航服务了,开个车去一个陌生的地方,来到一个不熟悉的地方我们都想着打开手机进行导航,当然我们使用的是我们自己的卫星。
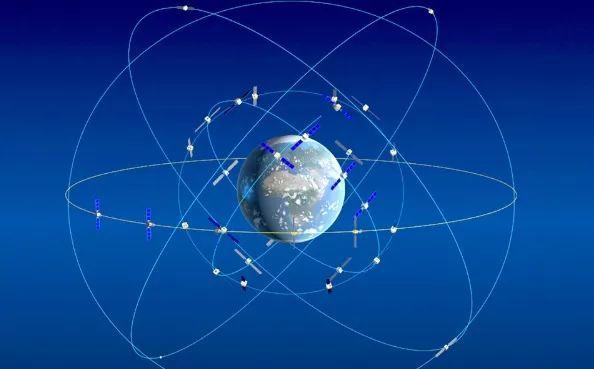
(图为轨道中的GPS卫星)
但是无论如何,都不能否认美国GPS曾经或者现在对于全球的贡献,很难想象如果没有GPS那么各种军用装备和民用设施该如何进行运转。率先把全球定位系统应用于战场的是美国人,早在上个世纪海湾战争期间,美国人就利用精确制导导弹打击对方,而精确制导的核心就是利用GPS进行定位导航。就现在来看,卫星通信、情报获取以及一些监视等都已经离不开全球定位系统的支持了。过分依赖是一种好事,在某种意义上来说也是一件坏事,其缺点也是致命的。首先就是GPS在发送和接受卫星信号的过程中非常容易受到电磁攻击和网络干扰,这样你还能说它很安全吗?除此以外,美国全球定位系统出于对整套系统成本的考虑,会在一些特定的时间,给一些特定的部分提供比较弱的信号波,结果就是这种信号波非常容易被拦截和监听,甚至敌方可以利用这些微弱电磁信号进行欺骗,从而对我方军事应用产生巨大的威胁。
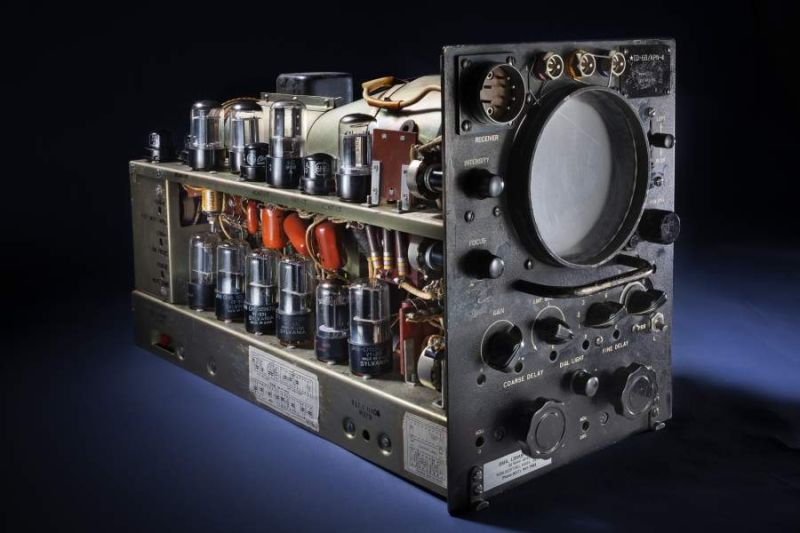
(图为罗兰C接收机,就这么看起普通的东西在当时也发挥了非常重要的作用)
其次,在水下等一些特殊的地方根本就无法接受GPS信号,一旦接收不到信号,那么对于严重依赖GPS进行作战的士兵以及武器装备来说意味着什么,我想不必明说大家也知道。说到这,我想起来了之前的一个例子,此前美军一个高级军官在一次电视节目中谈到一个观点,大概意思是他对于现在的美军士兵不会看纸质版地图这件事感到非常的惊讶和担忧,现在的任何人,当然包括士兵严重依赖着各种的电子产品,而一旦在战时这种电子的东西被敌方切断了怎么办。对于我们的警示是,对于士兵的基础训练永远不能拉下甚至取消。正是出于目前GPS应用的巨大危机,研制下一代不依赖GPS系统成为美军的高度共识。由美国国防部高级研究计划局和美军陆军新兴技术开发办公室开发的新一代导航系统将会在今年进行项目评估,其主要就是依靠甚低频,取代GPS。实际上,在卫星定位导航系统出现之前,人类最可靠的无线电导航技术就是采用甚低频波进行导航,也就是我们熟知的罗兰C。罗兰C系统是是上个世纪五十年代开始发展,到八十年代中期的时候,仅北大西洋公约组织建立的罗兰C导航台就已经能够覆盖北美、日本以及太平洋的主要部分了,在那个年代,罗兰C是北约的重要导航系统。
(图为民间车用GPS装置)
罗兰C全称叫远距离无线电导航系统,一般中文译为“罗兰”或者“罗拉”,这个系统是由二战时期的美国人开发的(又是美国人,难道二战时候开始美国人就开始主导这个世界了吗)。最开始的罗兰系统能够在2400公里的距离上进行导航定位,精确度为十英里。最开始美国人把罗兰系统应用于在大西洋上的美国舰队和远程巡逻机,后来太平洋战争爆发之后,美军太平洋舰队的作战飞机和舰船主要就应用这种导航系统了。后来,随着其他先进导航系统的出现,这一原始的导航最终落寞,2010年的时候,罗兰C和此前苏联研制的针对罗兰C的CHAYKA系统相继停止了服务。现在美国人又回过头来,开发新型增强型罗兰,这是在退步的基础上进步啊。(作者署名:利刃/WT)
U.S. GPS Navigation System Difficult to Retreat
June 25, 2018 18:19 Sina Military
0
The United States, which is currently the world’s comprehensive military capability, has much higher capabilities in the military than other countries. The general feeling is that when we started to equip a certain weapon or started to study a certain field, Americans have taken the lead in this aspect for many years of research, or did the Americans do all the leading countries? . After more than 60 years of development, the global positioning system, which is often referred to as GPS, has become the most complete global navigation system for human beings. GPS first originated from the US Department of Defense project in the late 1950s and was put into use in the mid-1960s. It began to provide real-time, all-weather and global navigation services to the global civilian market. Now for us ordinary people, we almost can't leave the navigation service. Open a car to a strange place and come to an unfamiliar place. We all want to open the mobile phone for navigation. Of course we use our own. satellite.
(The picture shows the GPS satellites in the orbit) (The picture shows the GPS satellites in the orbit)
But in any case, we cannot deny that the United States has once or now contributed to GPS globally. It is hard to imagine how various military equipment and civilian facilities would operate without GPS. It was the Americans who took the lead in applying the global positioning system to the battlefield. As early as during the Gulf War of the last century, Americans used precision guided missiles to strike at each other. The core of precision guidance is to use GPS for positioning and navigation. For now, satellite communications, intelligence acquisition, and some surveillance are all inseparable from the support of GPS. Excessive dependence is a good thing. In a sense, it is also a bad thing. Its shortcomings are also fatal. The first is that GPS is very vulnerable to electromagnetic attacks and network interference in the process of sending and receiving satellite signals. Can you say that it is safe? In addition to this, the U.S. Global Positioning System, for its consideration of the cost of the entire system, will provide relatively weak signal waves to certain specific parts at certain times. The result is that such signal waves are very easy to intercept and monitor, even The enemy can use these weak electromagnetic signals to deceive and thus pose a great threat to our military applications.
(The picture shows the Roland C receiver, so it seems that ordinary things also played a very important role at that time.) (The picture shows the Roland C receiver, so to see ordinary things at the time also played a very important role)
Secondly, in some special places such as underwater, it is impossible to receive GPS signals at all. Once signals are not received, what does it mean for soldiers and weapons and equipment heavily dependent on GPS for combat? I do not want to make it clear that everyone knows. Speaking of this, I remember one example. Before a senior military officer of the US military talked about a point in a television program, it probably meant that he felt very much about the fact that American soldiers do not read paper maps. Surprised and worried, anybody now, of course, including soldiers, is heavily dependent on various electronic products, and once this kind of electronic things are cut off by the enemy during the war. The warning for us is that the basic training for soldiers can never be pulled down or even cancelled. It is out of the huge crisis of GPS applications that the development of the next generation of GPS-independent systems has become a high level of consensus among the U.S. military. A new generation of navigation systems developed by the US Department of Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency and the US Army's Emerging Technology Development Office will conduct project evaluations this year, relying on very low frequencies to replace GPS. In fact, prior to the advent of satellite positioning and navigation systems, the most reliable radio navigation technology for humans was navigation using very low frequency waves, which is known as Roland C. The Roland C system began to develop in the 1950s. By the mid-1980s, only the North Atlantic Treaty Organization established the Roland C navigation platform that could cover major parts of North America, Japan, and the Pacific Ocean. Roland C is an important NATO navigation system.
(The picture shows a private car GPS device) (The picture shows a private car GPS device)
Roland C called the long-distance radio navigation system, generally translated into Chinese as "Roland" or "Roll", this system was developed by Americans during World War II (also American, did not start the World War II, the Americans began to dominate the world Yet). The first Roland system was able to navigate at a distance of 2400 kilometers with an accuracy of ten miles. Initially, Americans applied the Roland system to the US fleet and long-range patrol aircraft on the Atlantic Ocean. Later, after the outbreak of the Pacific War, the US Pacific Fleet's combat aircraft and ships mainly used such navigation systems. Later, with the advent of other advanced navigation systems, this original navigation was eventually abandoned. In 2010, Roland C and the former Soviet Union developed the CHAYKA system for Roland C and stopped its services. Now that the Americans have come back to develop a new type of enhanced Roland, this is a step backwards. (Author's signature: sharp/WT)
AMERICA is a JOKE! Regression back to WW1 technologies!
https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/201...ke-global-return-as-gps-backup-because-cyber/
Radio navigation set to make global return as GPS backup, because cyber
GPS killed the radio nav in 2010, but a high-def version is set to return.
Sean Gallagher - 8/8/2017, 2:40 AM
Enlarge / This is the way we used to find our way around.
National Air and Space Museum
Way back in the 1980s, when I was a young naval officer, the Global Positioning System was still in its experimental stage. If you were in the middle of the ocean on a cloudy night, there was pretty much only one reliable way to know where you were: Loran-C, the hyperbolic low-frequency radio navigation system. Using a global network of terrestrial radio beacons, Loran-C gave navigators aboard ships and aircraft the ability to get a fix on their location within a few hundred feet by using the difference in the timing of two or more beacon signals.
An evolution of World War II technology (LORAN was an acronym for long-range navigation), Loran-C was considered obsolete by many once GPS was widely available. In 2010, after the US Coast Guard declared that it was no longer required, the US and Canada shut down their Loran-C beacons. Between 2010 and 2015, nearly everyone else shut down their radio beacons, too. The trial of an enhanced Loran service called eLoran that was accurate within 20 meters (65 feet) also wrapped up during this time.
But now there's increasing concern about over-reliance in the navigational realm on GPS. Since GPS signals from satellites are relatively weak, they are prone to interference, accidental or deliberate. And GPS
can be jammed or spoofed—portable equipment can easily drown them out or broadcast fake signals that can make GPS receivers give incorrect position data. The same is true of the
Russian-built GLONASS system.
ARS TRENDING VIDEO
Talking Space and Robots with NASA's Terry Fong
Over the past few years, the US Coast Guard has reported
multiple episodes of GPS jamming at non-US ports, including an incident reported to the Coast Guard's Navigation Center this June that occurred on the Black Sea. South Korea has claimed on several occasions that
North Korea has jammed GPS near the border, interfering with aircraft and fishing fleet navigation. And in the event of a war, it's possible that an adversary could take out GPS satellites with anti-satellite weapons or some sort of cyber-attack on a satellite network.
As Director of National Intelligence Dan Coates
told the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence in May:
The global threat of electronic warfare (EW) attacks against space systems will expand in the coming years in both number and types of weapons. Development will very likely focus on jamming capabilities against dedicated military satellite communications (SATCOM), Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging satellites, and enhanced capabilities against Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), such as the US Global Positioning System (GPS).
The risk to GPS has caused a number of countries to take a second look at terrestrial radio navigation. Today there's broad support worldwide for a new radio navigation network based on more modern technology—and the system taking the early lead for that role is eLoran. As
Reuters reports, South Korea is preparing to bring back radio navigation with eLoran as a backup system for GPS, and the United States is planning to do the same.
Diff-e-q
The eLoran system gets its enhanced accuracy in much the same way that enhanced GPS gear squeezes greater accuracy out of the civil GPS signal for tasks such as surveying and mapping—by using
differential correction. A stationary receiver at a known fixed location checks the signal arriving from the beacon and measures the difference between its actual distance from the beacon and the distance calculated from the signal (based on the difference between the signal's timestamp and the time it was actually received).
In differential GPS, the differential information is broadcast by a base station at the known differential point; in eLoran, the data is fed back to the eLoran transmitter, and the transmitter applies the differential correction to its own signal. Since eLoran is regional, the differential calculation remains relatively accurate for its entire coverage area.
Because it uses low-frequency radio waves (in the 90 to 110 kHz range), it's not likely that you'll see eLoran integrated into your smartphone. While the antenna required for receiving eLoran signals is
relatively small (about two inches square), that's a fairly massive amount of real estate for a smartphone to dedicate to a backup navigation system. But that size could be reduced with some investment in antenna miniaturization. And while eLoran only works in two dimensions (it doesn't provide altitude data) and only works regionally (with a range of 800 miles), it has one major advantage over GPS: its powerful low-frequency signals are far less susceptible to jamming or spoofing. The signal from eLoran beacons is 1.3 million times stronger than GPS signals. A
2006 MITRE study found that attempts to jam or spoof eLoran would be highly unlikely to work.
"[eLoran] is a deterrent to deliberate jamming or spoofing, since such hostile activities can be rendered ineffective," said
Brad Parkinson, the retired US Air Force colonel who managed the original GPS development program, according to Reuters. A report Parkinson contributed to for an Institute for Defense Analyses Independent Assessment Team in 2014 found that "eLoran is the only cost-effective backup for national needs."
The administrations of both George W. Bush and Barack Obama pushed for a national eLoran system, but their efforts were never funded by Congress. However, the version of the Department of Homeland Security funding bill for 2018 just passed by the House of Representatives in July includes language calling for DHS to fund the construction and maintenance of a new eLoran system "as a complement to, and as a backup for" the GPS system. And the South Korean government already has pushed forward plans to have three active eLoran beacons by 2019—that's enough to provide accurate fixes for all shipping in the region should North Korea (or anyone else) attempt to block GPS again.