- Joined
- Aug 7, 2008
- Messages
- 1,204
- Points
- 48
https://www.pcworld.com/article/3397787/amd-ryzen-9-cpu-radeon-rx-5000-series-graphics-cards.html
News
AMD flexes 7nm muscle with a 12-core Ryzen 9 CPU and Radeon RX 5000 graphics cards
AMD challenges Intel and Nvidia with more efficient CPUs and GPUs, including our first look at the "Navi" brand and some great next-gen Ryzen parts.
 By Gordon Mah Ung
By Gordon Mah Ung Executive Editor, PCWorld | May 26, 2019 08:31 PM PT

The coremageddon has begun: AMD Monday dropped its long-awaited 12-core Ryzen 9 3900X at Computex on Monday, saying that it will outpace Intel’s 12-core CPUs for almost a third to half the price—and that’s just an inkling of AMD’s 7nm onslaught against Intel and Nvidia.
"To be a technology leader, you have to make big bets," said Lisa Su, AMD's chief executive, speaking at her first Computex keynote. AMD's biggest bet was in developing its chips for 7nm, and those bets are beginning to pay off.
During the kick-off keynote for Computex, AMD CEO Lisa Su unveiled:

[ Further reading: Best graphics cards for PC gaming ]
- “RDNA,” AMD’s new graphics architecture brand for its next-gen "Navi" core, which will be called the Radeon RX 5700 graphics card and go head-to-head with Nvidia’s GeForce RTX 2070.
- An 8-core, 16-thread Ryzen 7 3700X with stupidly good power efficiency of 65 watts.
- An 8-core, 16-thread Ryzen 3800X that all but erases any gaming deficits the CPUs have had versus the Intel competition.
- The world’s first PCIe 4.0-ready PC parts
- A dual-processor “Rome” Epyc server running laps on a dual-processor Intel Xeon Platinum 8280 server.
That's incredibly aggressive, especially when you consider that rival Intel wants $1,199 for its 12-core Core i9-9920X. Intel's core-count per dollar value looks even worse when you consider that AMD claims the Ryzen 9 3900X will outperform it by 14 percent in single-threaded tasks in Maxon’s new Cinebench R20 and 6 percent in multi-threaded tasks. It’s not just Cinebench R20 either. During the keynote, Su showed the Ryzen 9 3900X throwing down with $1,199 Core i9-9920X in a Blender demonstration too.
Even more impressively, the Ryzen 9 3900X will do it with a TDP rating of 105 watts, while the 14nm-based Core i9-9920X has a TDP of 165 watts. That’s not even mentioning that AMD typically measures its maximum thermal dissipation on a worst-case scenario while Intel’s TDP ratings shy toward what it calls normal use. Intel CPUs often exceed their formal TDP.
"We were not satisfied," Su said of the second-generation Ryzen. "Our engineering teams wanted to do more."
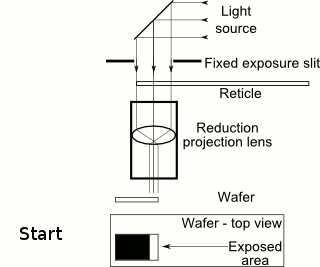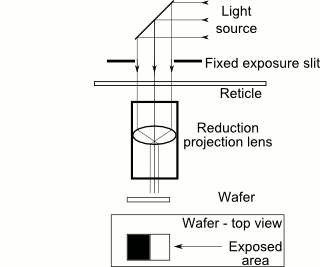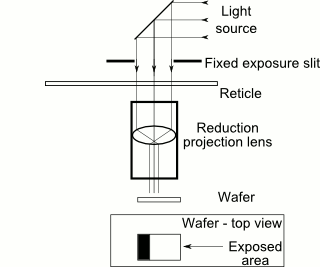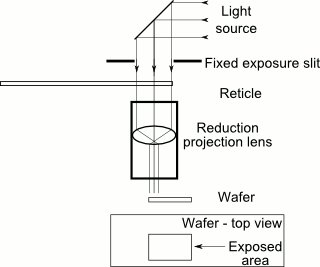
The new Ryzen 3000 chips will features PCIe 4.0 support. When combined with a PCIe 4.0 GPU and X570 motherboard, you can build an all PCIe 4.0 system.
The Ryzen 7 3700X’s TDP is just as stunning though. With 8-cores and 16-threads, it’ll produce just 65W of heat and hit a boost clock of 4.4GHz with a base clock of 3.6GHz. A comparable 8-core, 8-thread Core i7-9700K will put out 95 watts (and often exceed that).
While Su didn’t detail where all of the added performance comes from, a lot probably comes from the increased efficiency of the CPU. It had been rumored that the new Zen 2 cores would offer a very impressive 15 percent increase in Instructions Per Clock (or IPC). That rumor turned to be correct, as Su confirmed that the Zen 2 cores are 15 percent more efficiency the previous Zen cores.
Compared to the 95W Core i7-9700K, Su said the 65 watt Ryzen 7 3700X will outperform it by about 1 percent in single-threaded tasks (again using Cinebench R20 as the yardstick) and a smoking 28 percent in multi-threaded tasks. If you’re not impressed by a 1 percent performance difference, remember the Ryzen 7 3700X has a maximum boost clock speed of 4.4GHz while the Core i7-9700K’s Turbo Boost speed is 4.9GHz. And yes, the Ryzen 7 3700X is lower in cost too, with a list price of $329 compared to the $385 for the Core i7-9700K.
If you want to burn a little more power and create a little more heat, Su also teased a second Ryzen 7 3800X that pushes the TDP up to 105 watts. That takes the boost clock to 4.5GHz and the base clock to 3.9GHz.
Although AMD's Su didn't mention them in her keynote, AMD also announced several new Ryzen chips: the 8-core, 16-thread Ryzen 7 3800X (3.9GHz base/4.5GHz boost, 105W, $399); the 6-core, 12-thread Ryzen 5 3600X (3.8GHz base/4.4GHz boost, 95W, $249); and the 6-core, 12-thread Ryzen 5 3600 (3.6GHz base/4.2GHz boost, 65W, $199).
Ryzen’s gaming deficit looks to be erased
Compared to the fantastic Ryzen 7 2700X, the Ryzen 7 3800X has a 34 percent higher frame rate in League of Legends and Counter Strike: Global Offensive, AMD said. In PlayerUnknown’s Battlegrounds, it’s about 22 percent faster, with Overwatch coughing up 21 percent higher frame rates. AMD also said Dota 2 is 15 percent faster and Grand Theft Auto V is about 14 percent faster on the Ryzen 7 3800X.
AMD didn’t share comparisons against an Intel CPU, but with that sort of frame rate increase, it looks like one of the penalties AMD’s Ryzen chips have long held against Intel CPUs at lower resolutions might be nearly non-existent now (assuming AMD’s numbers come courtesy of a system with a fast GPU like the GeForce RTX 2080 and a common 1080p resolution).
The Ryzen 7 3800X offers about three percent more performance in single-threaded tasks than a Core i7-9700K and about 37 percent increased performance in multi-threaded tasks, AMD said.
But that’s not the CPU that AMD probably wants you compare the Ryzen 7 3800X against. That’s because Su also showed off the Ryzen 7 3800X outperforming Intel’s vaunted 8-core, 16-thread Core i9-9900K by about 1 percent in single-threaded tasks and about two percent in multi-threaded tasks. The Ryzen 7 3800X costs $399 though, while Intel’s Core i9-9900K tilts it at $484 or more on the street.
Why not show the $499 Ryzen 9 3900X against the $484 Core i9-9900K? We’d guess there’s a bit of gamesmanship there. While the 12-core Ryzen 9 3900X should easily clean Intel’s clock on multi-threaded tasks, it would also probably lose ground in single-threaded tasks. Of course, they’re both about the same price so it’s probably a wash. (AMD likely gives you a cooler too.)
Winning the race to PCI Express 4
Under the heat spreader, AMD officials told us the 12-core Ryzen 9 will be built using two Client Computing Devices (or CCDs) while the two 8-core Ryzen 7 chips will be built using single CCDs. The CPU is said to have 40 PCIe lanes. How that’s counted up isn’t clear, but it may also count up PCIe lanes in the new X570 chipset too. For its part, Asus appeared on stage to announce that it will have over 30 X570 boards.
We’re still looking for clarity but we’d guess that AMD is counting lanes located in the chipset controller, which typically aren’t as “good” as PCIe lanes in the CPU. We’ll update our story once we have more details.
Still, even if they’re in the chipset, they’re still PCIe 4.0 lanes though, right? To that point, AMD said with the PCIe 4.0 support in the new Ryzen chips, combined with the PCIe 4.0 in X570 motherboards, plus the PCIe 4.0 in its new Radeon RX 5700, you basically have all the makings of the “world’s first PCIe 4.0-ready gaming PC.”
Company officials are quite proud of that fact because it basically means that AMD already crossed the PCIe 4.0 finish line before Intel and Nvidia appear to even care to enter the race.
A 7nm Radeon RX 5700 too?
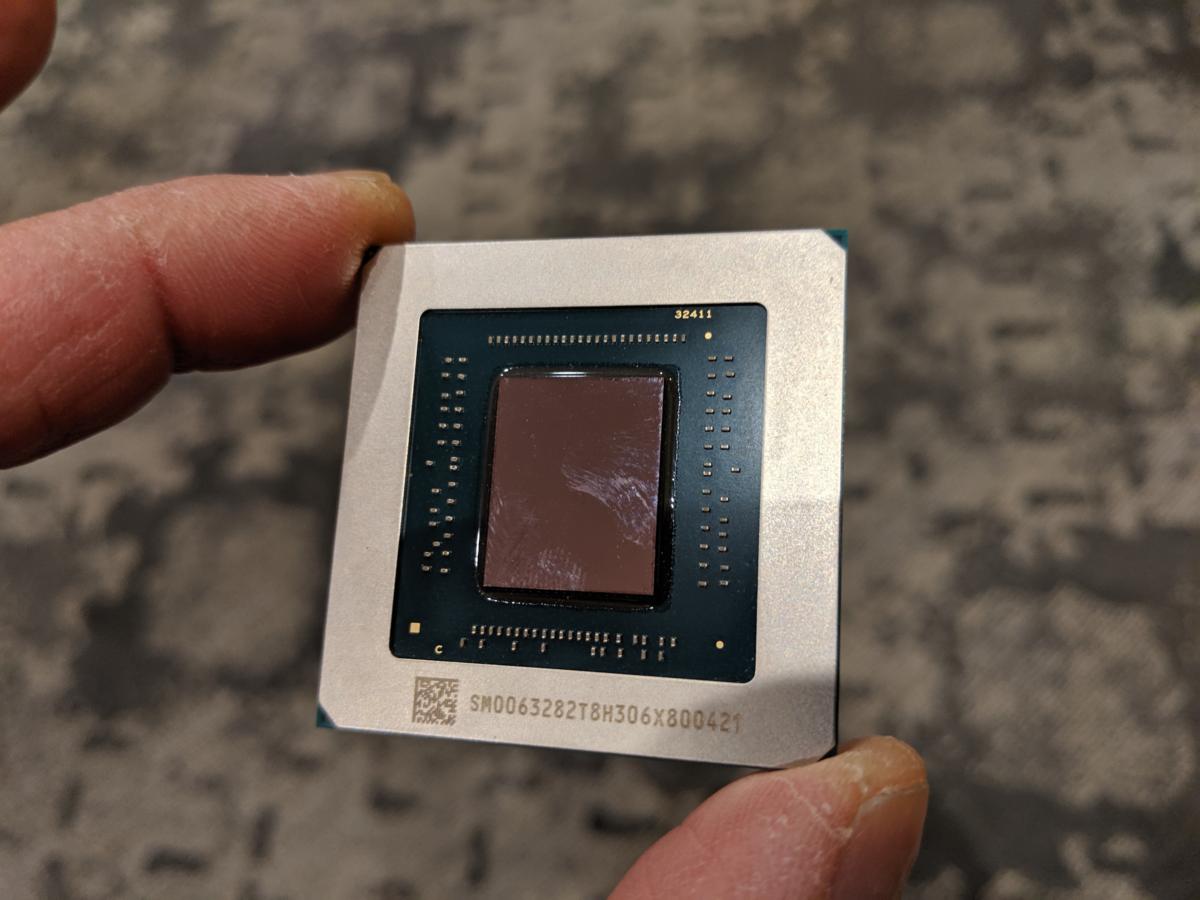

Gordon Mah Ung
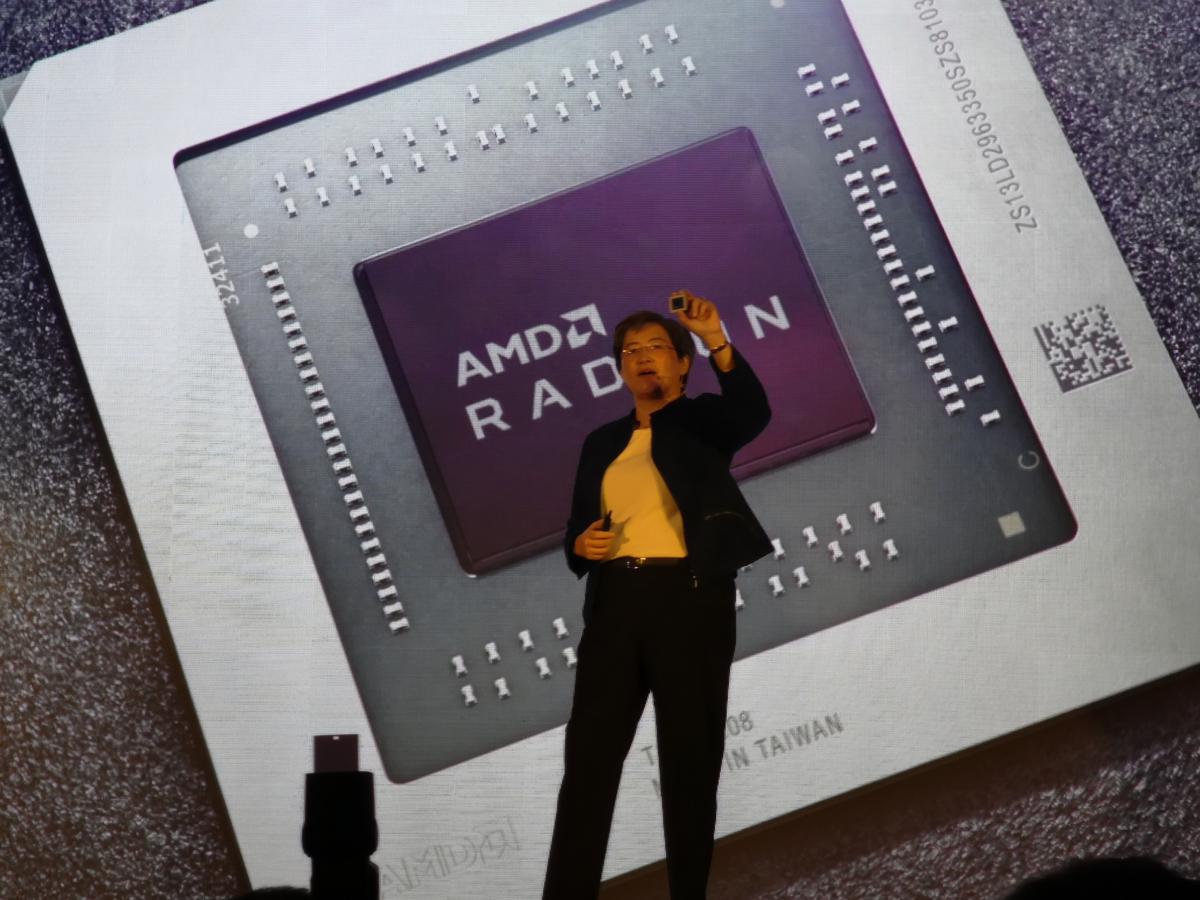
AMD’s new Radeon RX 5000-series of GPUs will offer 25 percent better performance per clock and 50 percent better performance per watt, the company said.
With Ryzen out of the way, AMD also teased its long-awaited “Navi” graphics architecture. According to Su, over 400 million gamers use the Radeon brand, from consoles to PCs to the data center.
RDNA, though, was created with the same thinking that powered the Zen brand: a ground-up rebranding for an entirely new architecture, Su said.
Su said its first 7nm Navi implementation will be part of the first Navi card: the Radeon RX 5000 family (with the 50-00 name deriving from the company’s milestone anniversary this year). The first GPU to hit the road will be the Radeon RX 5700, which will go toe-to-toe with Nvidia’s GeForce RTX 2070. As AMD’s first 7nm GPU, Su said the card will hit higher clock speeds and use less power than the current Radeon generation.
Mark Hachman/IDG
With a multi-level cache hierarchy, the Radeon RX 5700 offers greater bandwidth too. Su said the new Radeon RX 5000-series cards and their RDNA GPU architecture will offer 25 percent greater performance per clock and 50 percent greater performance per watt than its previous Vega-based cores. AMD also showed off a "preview" of Navi outperforming an RTX 2070 on Strange Brigade.
If you’re thirsty for more details on the Radeon RX 5700, you probably won’t have to wait much longer. Su said the Radeon RX 5700 cards should be available by July, and the company is holding an event at the annual E3 gaming show on June 10, where we’d expect to hear more details, including pricing, about Navi’s consumer form.
And yup, that July launch is on purpose. AMD said the new Ryzen processors are expected to be available on July 7 (psst, July is the 7th month) because, well, 7nm. As the first major chipmaker shipping 7nm chips to the public, AMD might as well rub it in.
To comment on this article and other PCWorld content, visit our Facebook page or our Twitter feed.
Related:
https://www.anandtech.com/show/1440...-cores-for-499-up-to-46-ghz-pcie-40-coming-77
AMD Ryzen 3000 Announced: Five CPUs, 12 Cores for $499, Up to 4.6 GHz, PCIe 4.0, Coming 7/7
by Ian Cutress on May 26, 2019 11:30 PM EST
- Posted in
- CPUs
- AMD
- Trade Shows
- Ryzen
- Zen 2
- Ryzen 3000
- Ryzen 3rd Gen
- Matisse
- Computex 2019
171 Comments + Add A
Comment

Today at Computex, AMD CEO Dr. Lisa Su is announcing the raft of processors it will be launching on its new Zen 2 chiplet-based microarchitecture. Among other things, AMD is unveiling its new Ryzen 9 product tier, which it is using for its 12-core Ryzen 9 3900X processor, and which runs at 4.6 GHz boost. All of the five processors will be PCIe 4.0 enabled, and while they are being accompanied by the new X570 chipset launch, they still use the same AM4 socket, meaning some AMD 300 and 400-series motherboards can still be used. We have all the details inside.
A lot of people have been after details about AMD’s next generation Ryzen platform for several months, ever since AMD teased the Matisse Ryzen 3000 design at CES back in January. Most of that information is coming out today, with Ryzen 9, Ryzen 7, and Ryzen 5 processors in the mix. All of these processors will be officially launched on July 7th (which is 7/7), correlating with the fact that the core chiplets of these products are built on TSMC’s 7nm process. This is technically a Sunday, but AMD doesn’t mind too much. In reality, it means users might even get them in the mail on the following Monday.
Before talking about features, let’s go straight into the CPU list, as that’s what most of you are here for.
AMD 'Matisse' Ryzen 3000 Series CPUsAnandTechCores
ThreadsBase
FreqBoost
FreqL2
CacheL3
CachePCIe
4.0DDR4TDPPrice
(SEP)Ryzen 93900X12C24T3.84.66 MB64 MB16+4+4?105W$499Ryzen 73800X8C16T3.94.54 MB32 MB16+4+4?105W$399Ryzen 73700X8C16T3.64.44 MB32 MB16+4+4?65W$329Ryzen 53600X6C12T3.84.43 MB32 MB16+4+4?95W$249Ryzen 536006C12T3.64.23 MB32 MB16+4+4?65W$199
The New Flagship: Ryzen 9 3900X
The Ryzen 3000 series will debut a new product tier for AMD: Ryzen 9. In this case, the Ryzen 9 3900X will be AMD’s first mainstream desktop 12-core processor. The processor is the only one of the group that uses two chiplets, in a 6+6 configuration. The 3900X will have a base frequency of 3.8 GHz, a turbo frequency of 4.6 GHz, and line up with 6 MB of L2 cache and 64 MB of L3 cache. This confirms that each chiplet has 32 MB of L3 cache, doubling what we saw on the first generation of the Zen microarchitecture. This CPU has a TDP of 105W, which for AMD processors is usually a good measure of all-core power consumption, and will be enabled with 24 PCIe 4.0 lanes (16 for GPU, 4 for storage, 4 for the chipset).
AMD 'Matisse' Ryzen 3000 Series CPUs
Ryzen 9AnandTechCores
ThreadsBase
FreqBoost
FreqL2
CacheL3
CachePCIe
4.0DDR4TDPPrice
(SEP)Ryzen 93900X12C24T3.84.66 MB64 MB16+4+4?105W$499
The Ryzen 9 3900X will have a suggested e-tail price of $499, and it will come with a cooler (more details in the coming weeks). AMD compared this processor in its presentations to Intel’s 12-core HEDT processor, the Core i9-9920X, which has an MSRP of $1199 and doesn’t come with a cooler.
In this comparison, AMD provided Cinebench R20 performance data comparing the two processors (it should be noted that we can’t confirm these results at this time). AMD states that in single thread performance, the 3900X beats the 9920X by +14%, and also wins in multi-threaded performance by 6%, all while having a lower TDP (165W vs 105W).

The Ryzen 9 3900X is the new mainstream desktop flagship, although AMD clearly has enough headroom on this design to enable a full 16 cores. Most users will expect this to come in the future, so it will be interesting to see if AMD will strategically play this card.
Mainstream Madness: Ryzen 7 at 65W
For the Ryzen 7 lineup, AMD is keeping this for the 8-core versions. These CPUs only have a single chiplet inside, and no dummy chiplet. Of the two CPUs in this segment, the one that gets a big shock from us is actually the cheaper model.
AMD 'Matisse' Ryzen 3000 Series CPUs
Ryzen 7AnandTechCores
ThreadsBase
FreqBoost
FreqL2
CacheL3
CachePCIe
4.0DDR4TDPPrice
(SEP)Ryzen 73800X8C16T3.94.54 MB32 MB16+4+4?105W$399Ryzen 73700X8C16T3.64.44 MB32 MB16+4+4?65W$329
The Ryzen 7 3700X is an eight core, sixteen thread CPU with a 3.6 GHz base frequency and a 4.4 GHz turbo frequency. It has 4 MB of L2 and 36 MB of L3 (half the L3 compared to Ryzen 9, because it only has one chiplet), but the amazing thing is that this chip has a TDP of just 65W. Just on paper, it looks like this processor is one of the most efficient x86 performance desktop processors ever made. This is likely the CPU configuration that AMD used in its Cinebench R20 demo back at CES, where it showed R20 equivalent multithreaded performance for 40% less system power. And the price for all this performance? Only $329. If I put my reviewer hat on and look at these specifications at a high level, the Ryzen 7 3700X promises to be the mainstream chip of choice for a substantial number of high-performance PCs this year.
Like with the Ryzen 9 3900X, AMD also ran a Cinebench comparsion with the 8 core Ryzen 3700X versus Intel's mainstream Core i7-9700K. Here they scored 4806, verus 3726 for the 9700K in R20's multithreaded test.
The other CPU in this bracket is the Ryzen 7 3800X. This is going to be the direct upgrade from the current Ryzen 7 2700X, comes with eight cores and sixteen threads, with a base frequency of 3.9 GHz and a boost frequency of 4.5 GHz. It doesn’t seem overly impressive compared to the 3700X with its larger 105W TDP for only a few hundred MHz more on the base frequency, however as we’ve seen with the 2nd Gen Ryzen, that extra TDP headroom usually helps with technologies like XFR that manage the boost frequencies. AMD hasn’t said anything new about how XFR or Precision Boost works in the new generation yet, we have to wait until nearer launch for that information. However the extra frequency and extra TDP will cost an extra $70: the Ryzen 7 3800X will retail for $399.
Budget Builds: Ryzen 5 with Six Cores
Not mentioned during the keynote, but discussed in the press release, AMD also gave information about its new Ryzen 5 processors.
AMD 'Matisse' Ryzen 3000 Series CPUs
Ryzen 5AnandTechCores
ThreadsBase
FreqBoost
FreqL2
CacheL3
CachePCIe
4.0DDR4TDPPrice
(SEP)Ryzen 53600X6C12T3.84.43 MB32 MB16+4+4?95W$249Ryzen 536006C12T3.64.23 MB32 MB16+4+4?65W$199
These are still very competitive – users can now buy a six-core processor for under $200. The processor frequencies are consummate with the position in the stack, along with the pricing, and both CPUs will support all the same technologies (PCIe 4.0, etc) as the bigger chips. These chips still use a single chiplet, not a dual chiplet design.
Performance Numbers
AMD provided some performance numbers to compare AMD to Intel CPUs. All of these tests are using Cinebench R20, which should be noted is a floating point rendering test that AMD already does well on, but there aren’t any specific optimizations here for each CPU.

Direct chip to chip comparisons put AMD’s single thread performance against Intel at +1%. Though it should be noted here that something like the Ryzen 7 3800X, which boosts to 4.5 GHz, is being compared to an Intel CPU that boosts to 5.0 GHz. That would put IPC on this test firmly in the hands of AMD. Multi-threading results are a similar scenario, although the margin of difference tends to drop the more cores that AMD has access to, perhaps because more cores are fighting to get to the memory with a slightly extended memory latency compared from Intel.
Comparing Zen 1 to Zen 2, AMD is promoting that the Ryzen 9 3900X offers +32% better single threaded performance over the Ryzen 7 1800X. Given that we saw a 40-52% IPC increase from pre-Zen to Zen 1, another +32% on single threaded performance is a good amount to have, although that 32% does include frequency uplift. When we get the chips in, we’ll do an obvious comparison test to find the IPC difference. In multi-threaded results, AMD is promoting +100% multithreaded performance, which is helped by +50% more cores, 2x better FP throughput per core, and higher frequencies.
Other Features and X570 Motherboards
Aside from the 7nm chiplets, and the monumental price comparison to Intel, there are some other features to mention. AMD is promoting a +15% direct IPC increase from Zen 1 to Zen 2, due to microarchitecture improvements and cache size doubling on the L3. The CPU has 24 PCIe 4.0 lanes: sixteen for the GPU (or other PCIe cards), four for storage, and four for the chipset. The four for storage will likely be linked to the top M.2 slot. Given that some companies are advertising PCIe 4.0 SSDs here at Computex, we expect more to follow in due course.
The new X570 chipset has 16 lanes, four for the upstream connection to the CPU, and twelve downstream for other devices. There is some discontinuity here – we heard from partners that AMD actually removed four PCIe lanes from the chipset design in order to bring the TDP of the chipset down from 15W to 11W; but the full-fat 15W version will be on the next editions of the high-end desktop (which would suggest that Threadripper isn’t dead, contrary to a lot of reporting – this is a question we will be asking Lisa Su later today). We have already seen a number of X570 motherboards ready to enter the market, and we expect around 25 new X570 models in total. It is clear that motherboard manufacturers are now getting serious on AM4 – some of these boards are likely to retail up to $600. These manufacturers are clearly expecting AMD to hit Intel hard, and have designed the motherboards to match the best that they make for Intel's CPUs.
One bit of information not disclosed is memory support, however given our discussions with AMD’s partners, this is likely to be DDR4-3200 in one module per channel mode. This is a small bump over 2nd Gen Ryzen, but still a welcome one. It will be interesting to see how the memory controller works on this design for pushing that frequency. The memory frequency and Infinity Fabric frequency are still linked as before, so bumping up the memory frequency has additional benefits.
Finally, the release date for all these CPUs is going to be July 7th. We’re waiting on AMD to disclose the sampling time frame, but our aim is to get our review up on day one. Suggestions for the review are most welcome.
We also have access to Dr. Lisa Su directly after the keynote today, and will write up our Q&A in due course. Stay tuned for that.
Want to keep up to date with all of our Computex 2019 Coverage?

Laptops

Hardware

https://sea.ign.com/pc/149612/news/amd-announces-next-gen-gpus-and-cpus-at-computex
PC / May 28, 2019
AMD Announces Next-Gen GPUs and CPUs at Computex
Navi and 3rd Gen Ryzen coming soon.
By Josh Norem
At Computex AMD has pulled the wraps off its next-gen GPU and CPU architectures, revealing its Navi GPU and third generation Ryzen CPUs as well. AMD CEO LIsa Su delivered a keynote address to kick off the hardware-focused trade show in Taipei, and showed off some of its upcoming hardware, with the promise of going more in-depth at E3 in two weeks time.
AMD Introduces Navi
The existence of AMD's Navi GPUs has never been a secret, but up until now all we knew about them was that they were going to be built on a 7nm node. It's such a non-secret that Sony has already stated it will be using Navi in the next-gen Playstation. At Computex, Su revealed the GPUs in the Navi lineup will be called the Radeon 5000 series; a nod to the company's 50th anniversary. They will also be the first GPUs built on a new RDNA microarchitecture (short for Radeon DNA), which is a departure from the previous GCN architecture that has powered everything from Hawaii up to Vega and the current Polaris cards. AMD announced it as the RX 5700 series, but pricing, clock speeds, and pricing were all TBD. However, they did say the GPUs will be available in July.

Dr. Su held up a Navi chip and pointed out that it was indeed a small chip, but said small is good and pointed to the fact that AMD is focusing on reduced power consumption; a pain point of previous AMD GPUs compared to Nvidia chips. As far as performance goes the company showed a demo of Strange Brigade running alongside an Nvidia RTX 2070, and noted the Navi chip was running ten percent faster. The RX 2070 is a $500 GPU, so if Navi comes out for $300 or so, that will indeed be quite an achievement. In a roundtable after the keynote AMD said it's not ruling out support for ray tracing, and that more info will be coming in June.

Dr. Su also pointed out that Navi GPUs are the first GPUs to use a PCI Express 4.0 interface, which double the amount of bandwidth compared to PCIe 3.0 GPUs we are all using now. Of course, to get access to that bandwidth you also need a motherboard and CPU that supports PCIe 4.0, which AMD announced as well.
3rd Gen Ryzen CPUs
The existence of 3rd gen Ryzen chips was also not a secret, but like the GPUs, we didn't know much about them other than their name. Dr. Su revealed these chips will use a new second-generation design that will offer a 15 percent instruction per clock (IPC) uplift compared to previous Ryzen chips. The first chip announced is the Ryzen 7 3700X, which is a 7nm CPU with 8-cores and 16-threads, running at 3.6GHz base clock with a 4.4GHz boost clock and surprisingly low 65w TDP. The company showed a demo of it running Cinebench R20 faster than the Intel Core i7 9700K, which is an eight-core/eight-thread CPU with a 95w TDP. The company spokesman said it was running "1/3 faster" than the Intel chip. Su said compared to the Intel chip, 3rd gen Ryzen would be "similar" in single-threaded performance, but approximately 28 percent faster in multi-threaded workloads. AMD announced the price of the 3700X at $329.

Lisa Su also announced the Ryzen 3800X, which is a 105w TDP GPU like the Intel 9700K. The company compared it to the i7 9900K in PUBG, and said it basically performs exactly the same. Previous AMD GPUs were mostly considered slightly inferior to Intel's chips when it comes to gaming, so AMD is looking to change that with its new CPUs. The 3800X will sell for $399.
Lisa Su also had a "one more thing" moment, and saved the best for last by announcing the Ryzen 9 series chips. This will be the first "mainstream" CPU with 12 cores and 24 threads running at 4.6GHz boost, all at 105w TDP. Dubbed the 3900X, AMD showed it running Blender much faster than the Intel Core i9 9920X HEDT chip, which is a 165w chip that sells for over $1,000. The AMD CPU ran the Blender demo 18 percent faster than Intel's chip, and will be priced at $499, severely undercutting Intel's pricing model in this segment. All of the new Ryzen processors will go on sale July 7th.

Stay tuned for more details on all the new AMD hardware, as much more should be revealed at E3 in a few weeks.
Josh Norem is IGN's Executive Editor for Tech. When he's not upgrading his PC he's trying to get his foster kittens adopted.
Share Tweet Submit