- Joined
- Aug 20, 2022
- Messages
- 28,052
- Points
- 113
Why is the hip-waist ratio important?

Medically reviewed by Daniel Wiznia, MD — Written by Lana Burgess — Updated on March 28, 2025
Waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), also known as waist-hip ratio, is the circumference of the waist divided by the circumference of the hips. Research associates a high WHR with certain health risks.
The WHR is a quick measure of fat distribution that may help indicate a person’s overall health. People who carry more weight around their middle than their hips may be at a higher risk of developing certain health conditions.
This article explains how to calculate WHR, how it may affect health, how a person can improve their ratio, and what else they should consider.
How to calculate waist-to-hip ratio

To find out their WHR, a person needs to measure both the circumference of their waist and their hips. Circumference means the distance around something.
To measure the circumference of their waist, a person should stand up straight and breathe out, then measure their waist just above the belly button with a tape measure. This measurement should be where the waist is the smallest.
People should be careful not to pull the tape measure too tight and remember to record the waist measurement before moving on to the hips.
To measure the circumference of their hips, stand up straight and wrap a tape measure around the widest part of their hips. Take the measurement where the ends of the tape measure overlap, again do not pull it too tight.
To calculate the WHR, divide the first measurement (waist circumference) by the second measurement (hip circumference).
Measurements can be in centimeters (cm) or inches (in) without affecting the ratio.
For example, if a person’s waist circumference is 80 cm (31.5 in) and their hip circumference is 90 cm (35.5 in), then their WHR ratio is 80 ÷ 90 = 0.89 cm (31.5 ÷ 35.5 = 0.89 in).
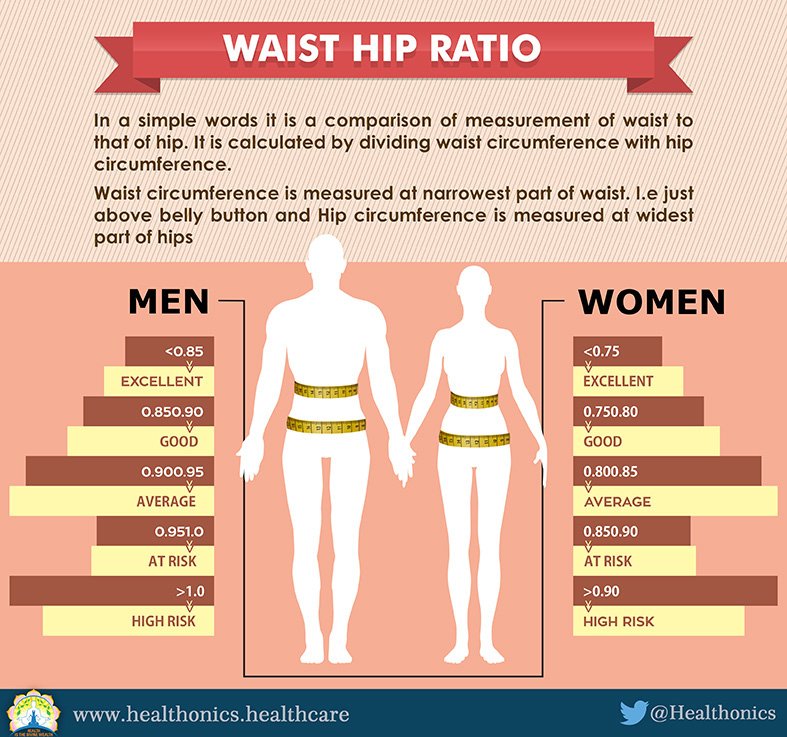
What is a healthy waist-hip ratio?
According to an older report from the World Health Organization (WHO), a high WHR may have an association with conditions that relate to overweight or obesity, including heart disease and type 2 diabetes.This may be the case even if other measures of weight, such as body mass index (BMI), are in the healthy weight range.
The WHO suggests that people may have abdominal obesity if their WHR is above the following:
- 0.85 for females
- 0.9 for males
The flaws of BMI
BMI is a calculation of a person’s body fat based on their height and weight. However, studies suggest it is a poor indicator of a person’s body fat percentage.It can be misleading because the measure does not account for overall body composition or capture information on the mass of fat in different body sites. The latter relates to both health and social issues.
BMI cutoff points were generated mostly from the white population, but body fat distribution differs by race and ethnicity.
For additional information, talk with your doctor about other body fat assessment methods.
Impact of waist-hip-ratio on health
Healthcare professionals may use a WHR measurement as an indicator of conditions such as obesity.Those with a high WHR carry more weight around their middle. Some people may describe their body shape as an “apple.”
Research suggests people who are “apple-shaped” may have a greater risk of certain health conditions, including:
- Chronic kidney disease: In a 2022 studyTrusted Source of 6,727 adults, WHR was a more accurate predictor of chronic kidney disease than other body metrics, including BMI.
- Heart attack: A 2024 review of 22 observational studies highlights a significant association between WHR and the risk of a heart attack.
- Obstructive sleep apnea: A 2022 studyTrusted Source suggests that WHR may be a risk factor for the severity of obstructive sleep apnea in males without obesity.
- Cardiovascular disease: A 2019 study associates abdominal fat with the long-term risk of cardiovascular disease in postmenopausal females with a healthy weight BMI.
- Type 2 diabetes: A 2024 study of 10,520 people in Iran highlights an association between high WHR and type 2 diabetes.
- Fertility: Another 2024 study highlights a positive association between WHR and the risk of infertility in females.
How to improve the ratio
If someone has a high WHR, they may be concerned about the related health risks. Achieving a moderate weight and reducing their WHR may help to lower these risks.Strategies that can lead to safe and effective weight loss include:
- setting realistic goals, such as aiming to lose 5% to 10%Trusted Source of a person’s starting weight within six months
- practicing portion management
- getting regular exercise
- eating a balanced, healthful diet
- getting enough sleep
People can also speak with a healthcare professional about other options that may be available to them, including weight loss medications, such as GLP-1 antagonists including semaglutide (Ozempic, Rybelsus), or surgeries.
People should also be mindful and cautious of weight loss programs that make unrealistic or false claims, such as targeted weight loss in a specific body part or losing a lot of weight in a very short period.
Waist-hip-ratio considerations
While a person’s WHR is a useful measure for some health markers, it is important to remember that it is not foolproof.People may take inaccurate measurements or make a mistake when doing the calculation. In addition, if someone has a high BMI or is less than 5 feet tall, their WHR may be less meaningful.
If people have concerns about their weight or abdominal fat, they can speak with a healthcare professional about its health impacts and whether they may benefit from weight changes.
It is important to note that a WHR is not suitable for measuring the health of children. Healthcare professionals may only suggest it as a way to monitor weight for adults.
Summary
The waist-hip ratio divides a person’s waist circumference by their hip circumference to measure their level of abdominal fat.However, it is possible to make mistakes when measuring and calculating WHR, so people should not rely on it as a sole measure of obesity or health risk. Doctors may use this measurement with other bodyweight metrics, such as BMI.
If people have concerns about their weight or WHR, they can speak with a healthcare professional. A doctor may suggest lifestyle changes to achieve a moderate weight and reduce abdominal fat.

-1080x1080-(1).png?sfvrsn=794a9994_5)