- Joined
- Aug 20, 2022
- Messages
- 26,421
- Points
- 113
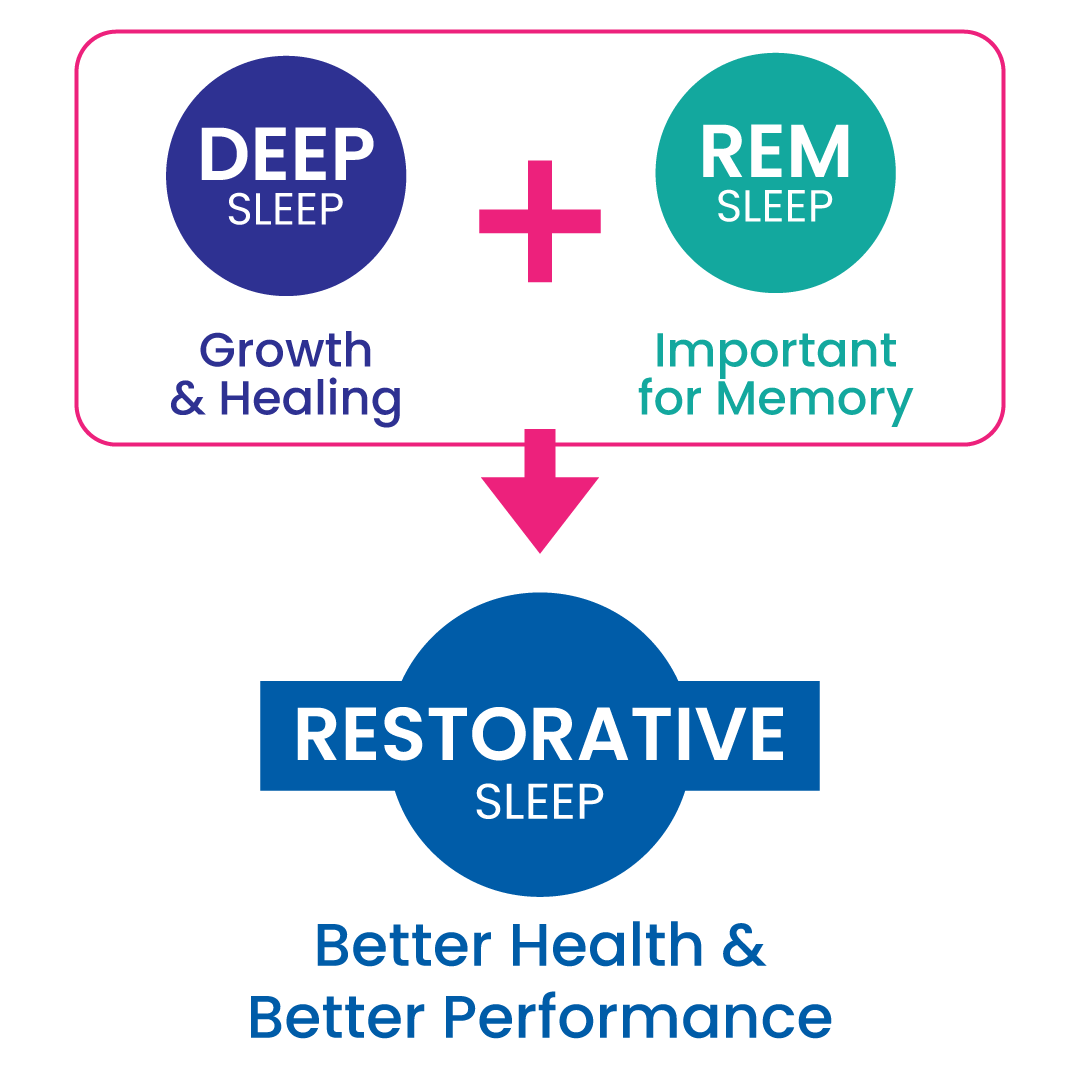
Restorative sleep is when your body and mind fully recover and rejuvenate during sleep, allowing you to wake up feeling refreshed and ready for the day. This type of sleep is characterized by time spent in deep sleep (NREM stage 3) and REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, which are crucial for physical and mental restoration, respectively.
Deep sleep (NREM stage 3): This is the physically restorative stage where the body repairs and replenishes itself. During deep sleep, your breathing, heart rate, and body temperature are at their lowest, and your muscles are relaxed. This stage is important for tissue growth, hormone release, immune system strengthening, and brain detoxification.
REM sleep: This is the mentally restorative stage where most of your dreams occur, and short-term memories are converted into long-term memories. It's also when the brain reorganizes and consolidates information, contributing to cognitive function and learning.
Why restorative sleep is important:
- Physical recovery:
Deep sleep helps repair tissue, restore energy, and support various bodily functions. - Cognitive function:
REM sleep is crucial for memory consolidation, learning, and cognitive performance. - Mental well-being:
Restorative sleep contributes to emotional regulation, stress reduction, and overall mental health. - Hormonal balance:
Sleep plays a vital role in regulating hormones related to growth, metabolism, and stress response. - Immune system support:
Adequate sleep is essential for a healthy immune system and resistance to illness.
- Physical recovery:
- Waking up feeling refreshed and energized.
- Being able to concentrate and focus throughout the day.
- Experiencing improved mood and emotional stability.
- Having a good memory and recall.
- Sleep environment: A dark, quiet, and cool room can promote better sleep.
- Sleep schedule: Maintaining a regular sleep-wake cycle is important for regulating your body's natural sleep-wake rhythm.
- Caffeine and alcohol: These substances can disrupt sleep patterns and reduce the quality of restorative sleep.
- Stress and anxiety: Managing stress and anxiety can help improve sleep quality.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine: This could include taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to calming music.
- Limit screen time before bed: The blue light emitted from electronic devices can interfere with sleep.
- Avoid large meals and caffeine before bed: These can disrupt your sleep cycle and make it harder to fall asleep.
- Ensure your sleep environment is conducive to sleep: Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool.
- Consider talking to a healthcare professional if you have persistent sleep problems: They can help identify any underlying issues and recommend appropriate solutions.



