- Joined
- Oct 9, 2013
- Messages
- 50
- Points
- 0
Global flight-tracking satellites deal signal an end to mysterious missing planes like MH370
Geneva meeting ends in accord for coordinated action signed by over 160 countries
PUBLISHED : Thursday, 12 November, 2015, 2:14pm
UPDATED : Friday, 13 November, 2015, 2:37am
Agence France-Presse in Geneva

A woman writes a message on a board for passengers onboard missing Malaysia Airlines Flight MH370 and their family members. Photo: Reuters
World nations struck a landmark deal Wednesday on using satellites to track flights, which could prove key to preventing a repeat of the mysterious disappearance of flight MH370 in March 2014.
Countries reached an accord at a conference hosted by the UN’s International Telecommunication Union (ITU) that aimed to improve on the current civilian flight-tracking system which relies on ground-based radars.
“In reaching this agreement ... ITU has responded in record time to the expectations of the global community on the major issue concerning global flight tracking,” the organisation’s secretary general, Zhao Houlin, said in a statement.
The ITU statement made clear the deal was driven by the disappearance of Malaysia Airlines flight MH370 which was lost en route from Kuala Lumpur to Beijing with 239 people on board.

French gendarmes inspect a piece of plane debris on the French Indian Ocean island of La Reunion on July 29. The disappearance of Malaysia Airlines Flight MH370, which vanished last year in one of the biggest mysteries in aviation history, prompted the signing of the new accord. Photo: Reuters
That tragedy “spurred worldwide discussions on global flight tracking and the need for coordinated action,” the organisation said.
Representatives of more than 160 nations attended the talks, known as the World Radiocommunication Conference (WRC).
One of the goals was to determine the technical requirements for a tracking system capable of providing complete surveillance of global airspace.
The ITU said a frequency band previously used to transmit signals from aircraft to terrestrial stations would be enabled to send transmissions from aircraft to satellites.

The shadow of a Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF) P3 Orion maritime search aircraft is seen on low-level clouds as it flies over the southern Indian Ocean looking for missing Malaysian Airlines flight MH370 last March. Photo: Reuters
This change will enable “real-time tracking of aircraft anywhere in the world,” said Francois Rancy, director of the ITU Radiocommunication Bureau.
The new system is expected to be fully implemented in 2017, but Rancy noted that most planes already have the necessary equipment, so compliance will not pose major logistical hurdles.
US Ambassador Decker Anstrom praised the deal, saying it would “enable better tracking and location of aircraft that otherwise could disappear from terrestrial tracking systems.”
The UN’s International Civil Aviation Organization has previously voiced support for a proposal that would make it obligatory for airlines to track their aircraft using a system that gives its location at 15-minute intervals.
The ground-based radars currently in use can track a plane but coverage is sketchy and fades when aircraft are out at sea or they are flying below a certain altitude, shortcomings that intensified the need to develop a better system.
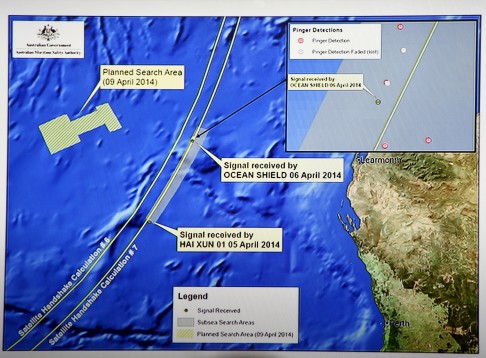
Graphics on a TV screen shows the current search area for the missing Malaysia Airlines flight MH370, during a media briefing at Dumas House in Perth in this April 9, 2014 file photo. Australian authorities searching for the wreckage of the Malaysia Airlines jet should urgently re-investigate two areas in the remote Indian Ocean where sonar pictures show what could be debris from the plane, deep-sea search experts said on October 20, 2015. REUTERS/Richard Polden/Files
Finding consensus on other agenda items at the WRC could prove tougher, however, including discussions on using existing satellites to provide coordinates to civilian unmanned aircraft systems, or drones.
Countries are also discussing whether to shift the way radio spectrum is used by different radio transmission technologies and applications.
The United States among others wants to see a reallocation of a significant amount of spectrum for mobile technologies and emerging 5G mobile networks.
But this is a touchy subject, as most of the high-quality spectrum is today used by broadcasters, and striking a deal by the end of the conference on November 27 is not guaranteed.
